Built with developer experience in mind, Tensorkube simplifies the process of deploying serverless GPU applications. In this guide,
we will walk you through the process of setting up Tensorkube and deploying a FastAPI app on it.
This tutorial is split into 3 parts:
- Setting up your Tensorkube Cluster
- Time Required: 25-30 minutes
- Prerequisites:
- You must have appropriate AWS permissions to create resources on your AWS account. Please refer to the list of permissions.
- Setting up your CLI
- Time Required: 5-10 minutes
- Prerequisites:
- You must have Python and pip installed on your machine
- We support Python versions from
3.7 to 3.11. Make sure that your virtual environment is set up with one of these versions.
- Deploying your first Tensorkube App
- Time Required: 10-15 minutes
- Note: To deploy with GPUs, you must have GPU quotas (G and Vt or P instances) on your AWS account
Cluster Setup
We have automated the process of setting up a cluster so that you can create it with minimal effort.
Please visit https://app.tensorfuse.io/ and keep this tutorial open in another tab if you need to refer to it.
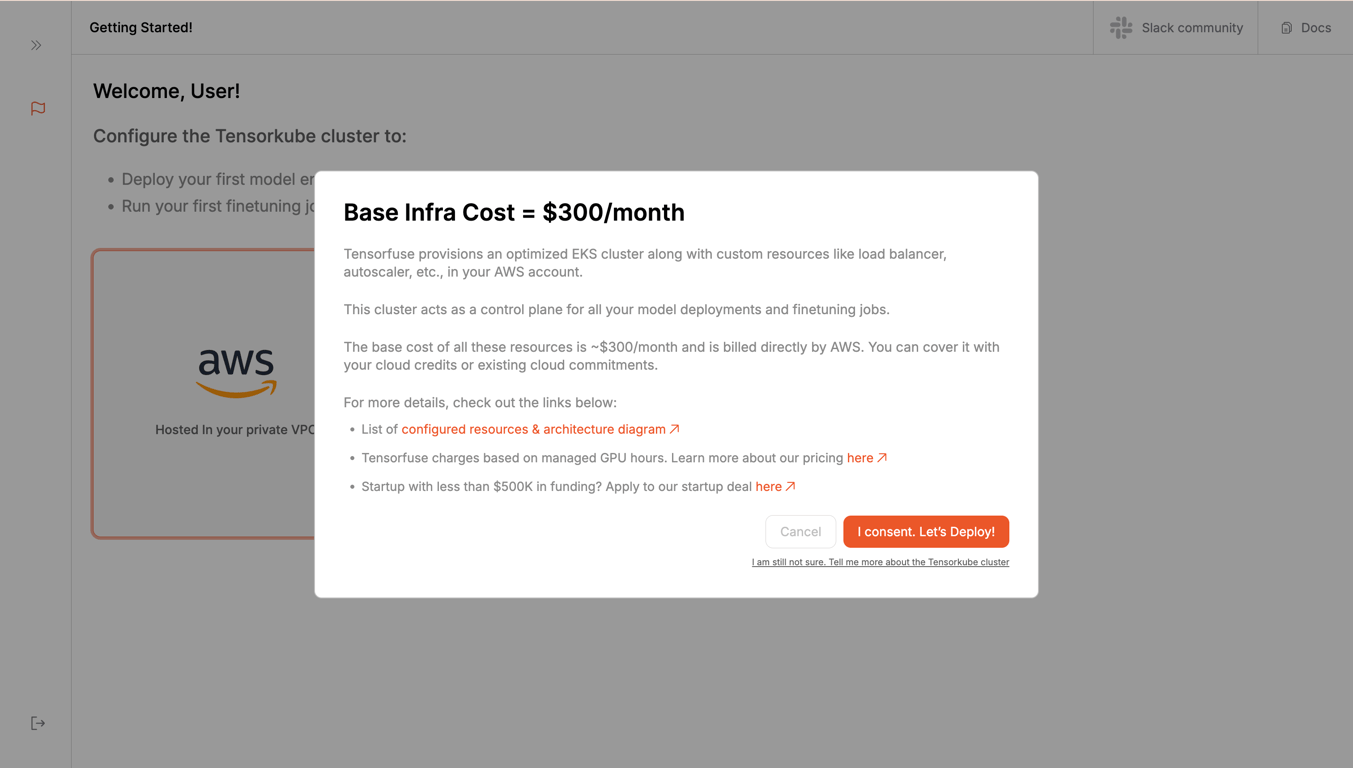
Tensorfuse runs on two CPU machines on your cloud account. The base cost of which comes out to be USD 300 per month.
Step 1: Login
Login/Signup with your Gmail or workspace account.
Step 2: Select your cloud provider
Currently, we only support AWS as a cloud provider.
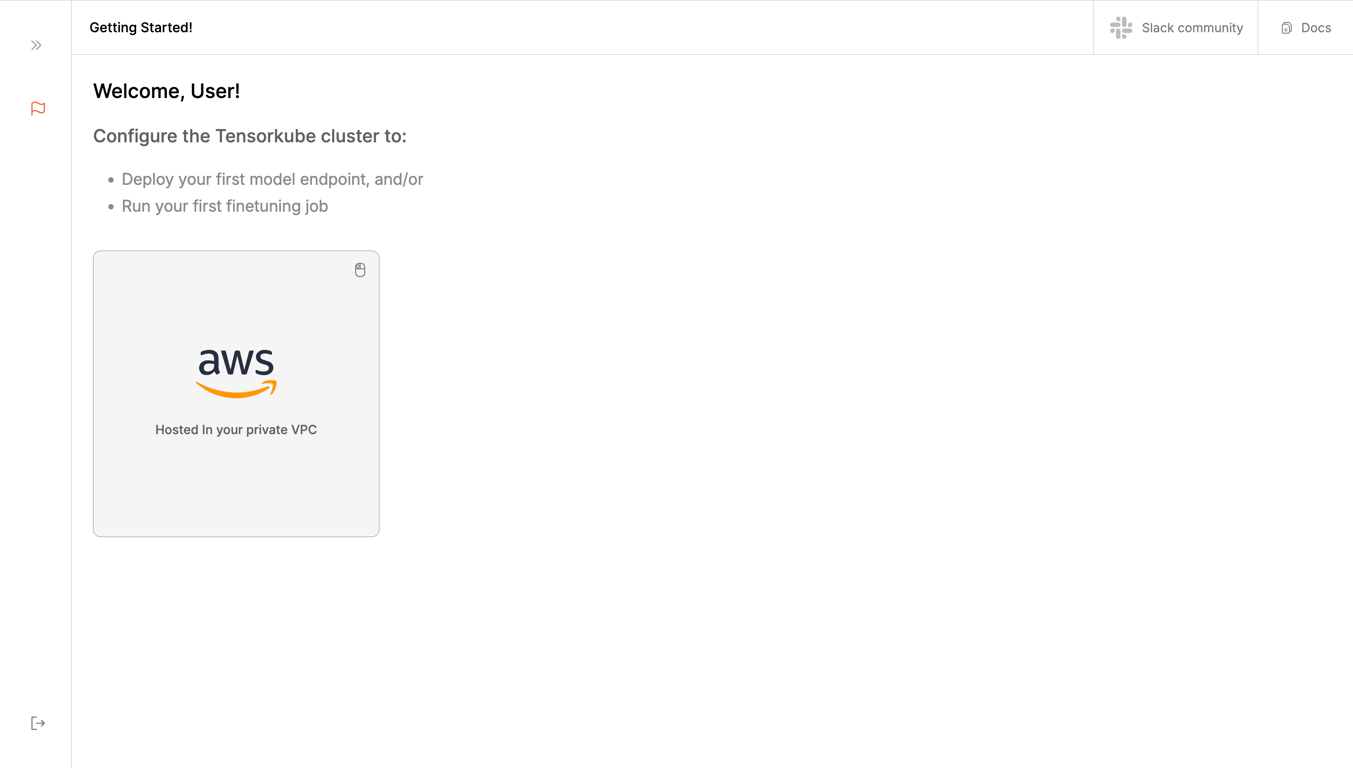 Please select AWS.
After this, you will be shown a consent popup. Read the terms and conditions and click on the
Please select AWS.
After this, you will be shown a consent popup. Read the terms and conditions and click on the I consent, Let's Deploy button.
Step 3: Grant Permissions to Tensorfuse
Login to your AWS account using the login button provided. Please note that you will be redirected to the AWS console. After you are done with the login and can see your AWS console, click on the Continue button.
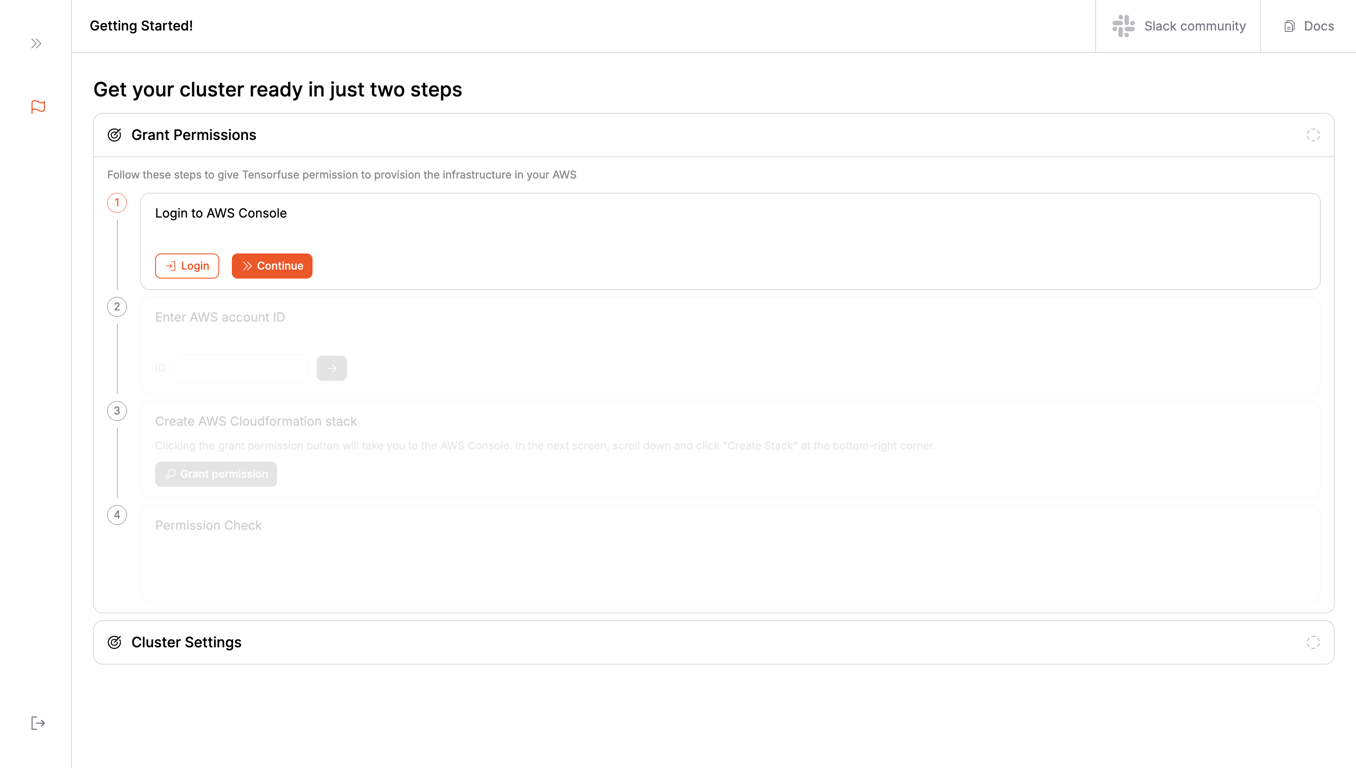 For the next step, we need to grant permissions to Tensorfuse to create resources on your behalf. For this, we need to know your
For the next step, we need to grant permissions to Tensorfuse to create resources on your behalf. For this, we need to know your AWS account ID. You can find that in the top right corner of your AWS console.
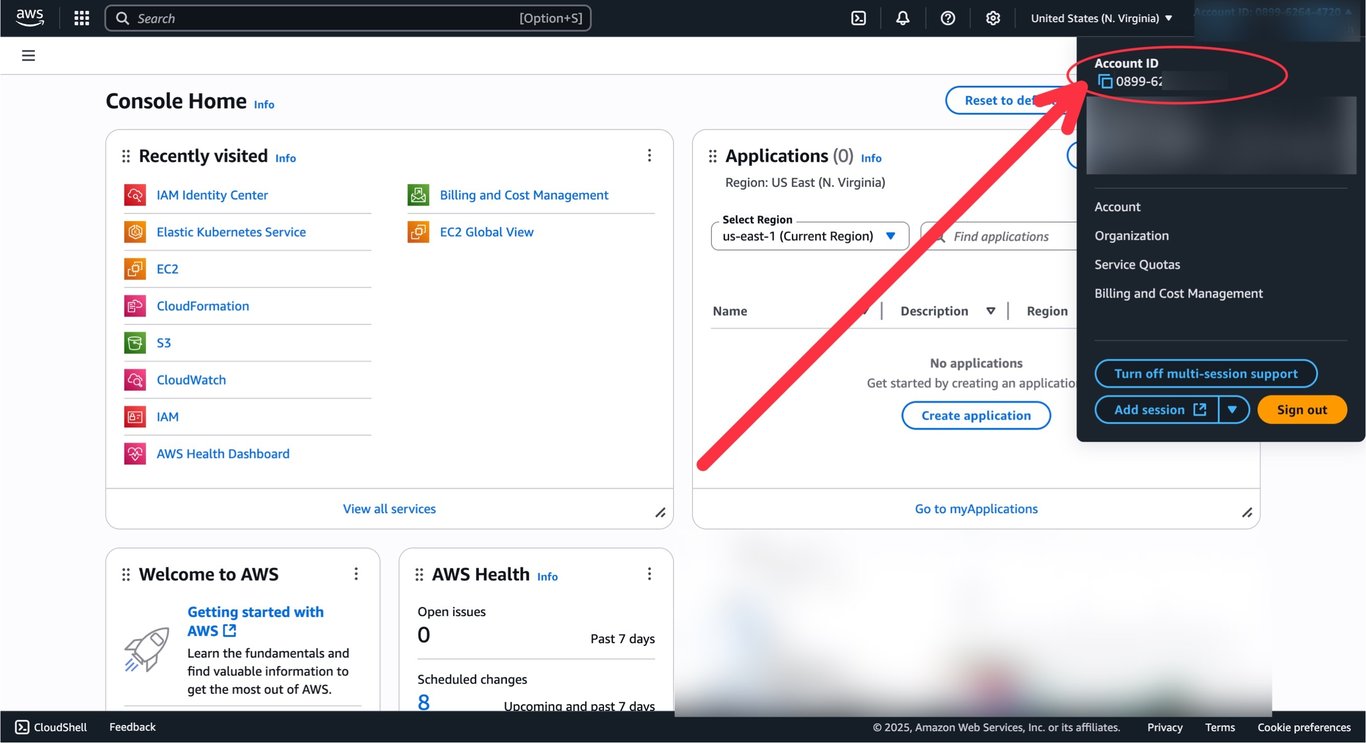 After you’ve entered your account ID, click on the
After you’ve entered your account ID, click on the Grant Permissions button.
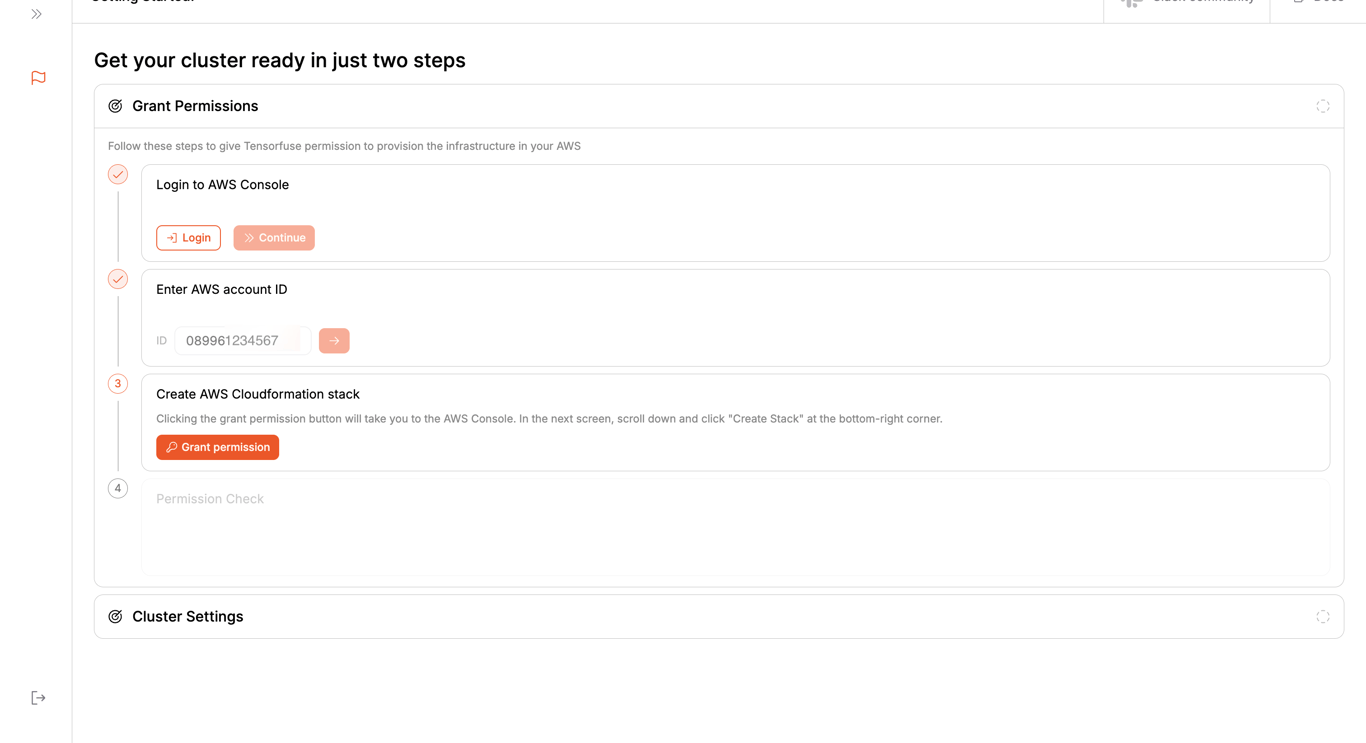 This will take you to your AWS console to create a permission stack. Scroll down to the bottom of the page, click on the checkbox, and click on the
This will take you to your AWS console to create a permission stack. Scroll down to the bottom of the page, click on the checkbox, and click on the Create Stack button.
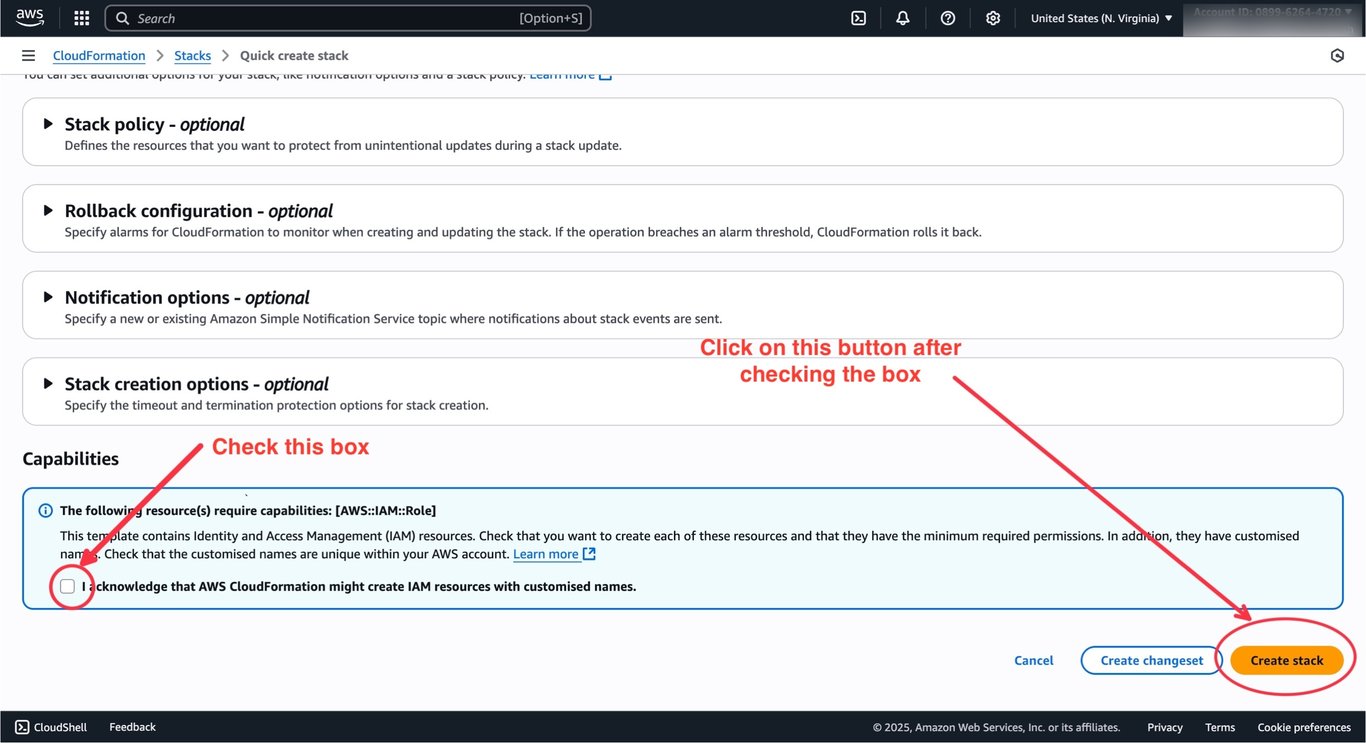 Click on the
Click on the Create Stack button.
After this, we will automatically create some granular roles with minimal access to create and manage resources on your behalf.
You will have to create the permission stack within a few minutes. The function times out after 10 minutes. If not created, you will need to refresh the page and re-run the permissions flow.
TensorkubeAccessStack and TensorkubeGranularPermissionsStack permission stacks are created successfully, you will be able to create your cluster.
Step 4: Create Cluster
Select the region where you want to create your cluster.
Enter an alert email address where you want to receive notifications about your cluster.
Please note that you will receive an email from AWS about the subscription. Accept it if you want to receive notifications.
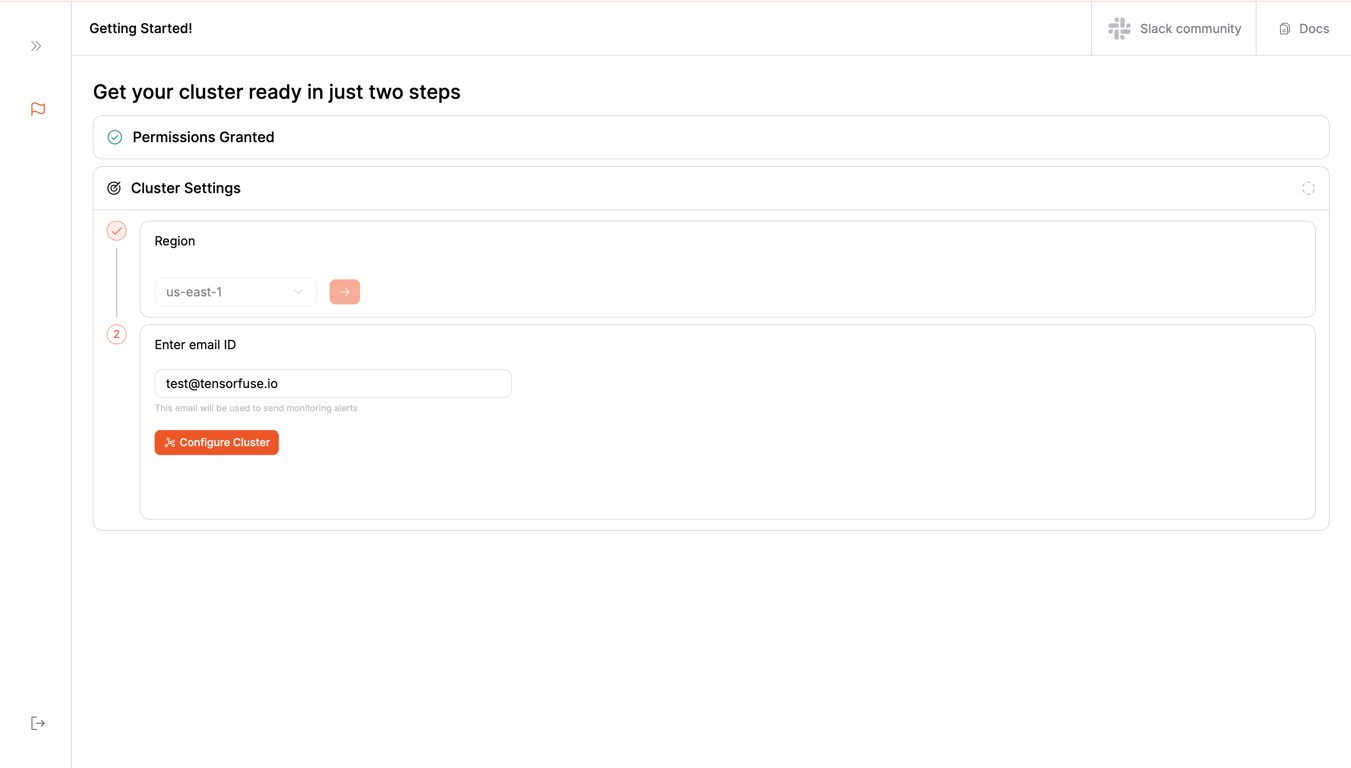 Click on the
Click on the Create Cluster button.
This will take around 25-30 minutes to complete.
You can go for a walk or brew a coffee and come back later. We will take care of everything for you.
Setting up your CLI
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
- Python and pip installed on your machine
- We support Python versions from
3.7 to 3.11. Make sure that your virtual environment is set up with one of these versions.
- AWS CLI installed on your machine. You can refer to this guide to install it.
We only support Python versions from 3.7 to 3.11. If you use a different version, there’s a chance that things will not work as expected.
If you’re an IAM user:
aws configure --profile tensorfuse
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=your_access_key_id
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=your_secret_access_key
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=us-east-1
If you’re an Identity Center User:
aws configure sso --profile tensorfuse
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=your_access_key_id
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=your_secret_access_key
export AWS_SESSION_TOKEN=your_session_token
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=us-east-1
Installation
First, install the tensorkube Python package:
Following this, run the following command to login to Tensorfuse and get your token.
You just have to sign in using your Google Workspace account and Tensorfuse will automatically manage the token for you.
Sync your local environment with the cloud environment
After this, run the following command to sync your local environment with the cloud environment:
This command will sync your cluster (created in the previous step) with your local environment.
Deploying your first Tensorkube app
Each Tensorkube deployment requires two things - your code and your environment (as a Dockerfile).
Code files
Let’s create a simple FastAPI app and deploy it on Tensorkube. Before deploying your app, ensure you have a /readiness endpoint configured in your FastAPI app.
Tensorkube uses this endpoint to check the health of your deployments. Given below is a simple FastAPI app that you can deploy:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/readiness")
def readiness():
return {"status": "ready"}
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"message": "Hello, World!"}
Environment files
Add your Python dependencies to requirements.txt:
Next, create a Dockerfile for your FastAPI app. Given below is a simple Dockerfile that you can use:
# Use an official Python runtime as a parent image
FROM python:3.9-slim
# Set the working directory in the container
WORKDIR /app
# Copy the current directory contents into the container at /app
COPY . /app
# Install any needed packages specified in requirements.txt
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# Make port 80 available to the world outside this container
EXPOSE 80
# Run app.py when the container launches
CMD ["uvicorn", "main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "80"]
Tensorfuse uses your entire project folder as the build context so make sure that no other files directories are present in the folder.
Users make the mistake of creating python env directories inside the project folder which then interferes with the build process.
If you have other things in the folder, make sure that you make a .dockerignore file and put the irrelevant stuff in that file.
Deploying the app
This is the easiest part. Navigate to your project root and run the following command:
Voila! Your first deployment is ready to go. You can access your app at the URL provided in the output.
Deploying with GPUs
If you want to deploy your app with GPUs, you can specify the number of GPUs you want to use in your deployment:
You will need to have a GPU quota on your AWS account to deploy with GPUs.
tensorkube deploy --gpus 1 --gpu-type a10g
--gpu-type argument supports all the GPU types that are available on AWS. You can find the list of supported GPU types here.
Check the status of your deployment
You can list all your deployments using the following command:
tensorkube deployment list
tensorkube deployment describe <deployment_id>

